Alcohol Liver Disease (ALD) encompasses a range of liver conditions resulting from excessive alcohol consumption. It’s crucial to understand how ALD develops, its effects on your health, and strategies for prevention or management. Whether you’re looking for information for yourself or a loved one, being informed can significantly impact your health journey.
What Are the Different Stages of Alcohol Liver Disease?
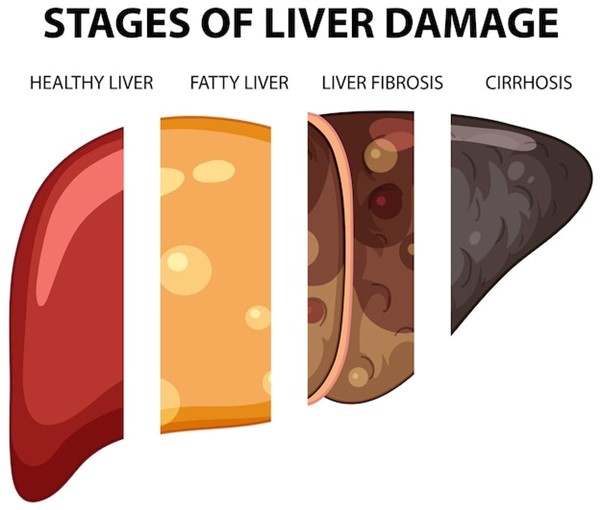
ALD progresses through three key stages, each indicating increasing liver damage:
- Fatty Liver (Steatosis): This initial stage involves fat accumulation in liver cells. Often asymptomatic, it serves as an early warning that the liver is under stress.
- Alcoholic Hepatitis: At this stage, the liver becomes swollen resulting in symptoms such as nausea, abdominal discomfort, jaundice (the yellowing of the skin and eyes), and fever. Alcoholic hepatitis can vary in severity from mild to severe.
- Alcoholic Cirrhosis: The most advanced stage involves chronic liver damage that results in scarring (cirrhosis). This stage can lead to serious complications, including liver failure, internal bleeding, or liver cancer.
What Causes Alcohol Liver Disease?
The primary driver of ALD is prolonged, heavy alcohol consumption. However, several other factors also increase the risk of developing this condition:
- Alcohol Consumption Levels: Regularly drinking above the recommended limits significantly increases your risk of ALD.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may inherit a genetic susceptibility that makes them more susceptible to liver damage from alcohol.
- Dietary Habits: Poor nutrition can compromise liver health, making it more vulnerable to damage.
- Preexisting Health Conditions: Conditions such as obesity, hepatitis, or other liver diseases can elevate the risk of developing ALD.
How Can You Prevent Alcohol Liver Disease?
Preventing ALD is vital for maintaining optimal liver health. Here are some effective strategies:
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Adhering to recommended alcohol consumption guidelines is crucial for reducing risk.
- Follow a Balanced Diet: A healthy diet supports overall liver function and resilience.
- Stay Hydrated: Staying well-hydrated supports the liver in carrying out its vital functions.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Routine medical examinations can help identify early signs of liver stress or damage.
How is Alcohol Liver Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosing ALD typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging techniques, such as ultrasounds. If you experience symptoms like jaundice or persistent abdominal pain, it is always essential to seek medical attention promptly, as early intervention can prevent significant damage.
What Are the Treatment Options for Alcohol Liver Disease?
Managing ALD generally requires lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medical treatment:
- Cease Alcohol Consumption: Stopping drinking is the most critical step to prevent further liver damage and, in early stages, may even reverse some effects.
- Medications: Healthcare providers may prescribe medications to reduce inflammation or address complications associated with cirrhosis.
- Nutritional Support: Collaborating with a dietitian to establish a liver-friendly diet is crucial for recovery.
Taking control of your liver health is vital, especially when it comes to preventing and managing Alcohol Liver Disease. For expert guidance and personalized treatment plans, turn to the Life Institute of Gastroenterology & Gynaecology. Our team is dedicated to supporting your journey toward better liver health. Schedule a consultation today to prioritize your well-being.