Gallstones
- Home
- Gallstones
Gallstones Frequently asked questions
What is the gallbladder and what does it do?
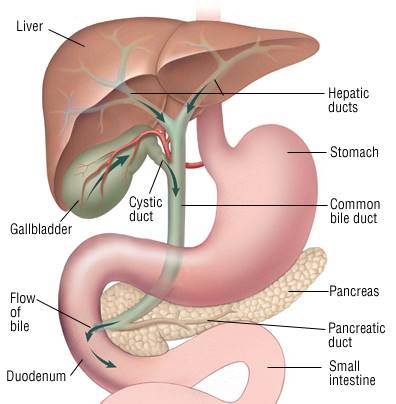
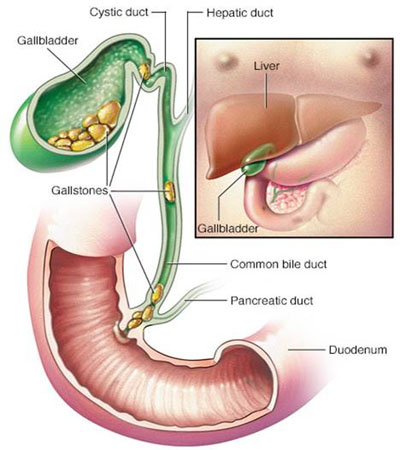
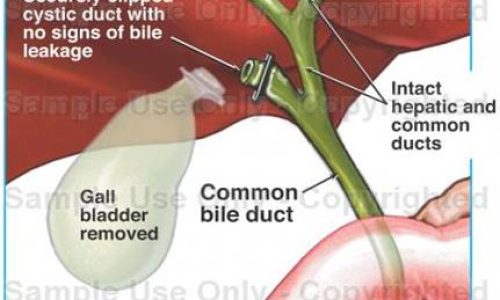
Bile is synthesized with in liver and drained through Right and Left Hepatic ducts that joins to form Common bile duct (CBD). The gall bladder is a pear-shaped bag that lies under the liver, beneath the rib cage, on the right side of the abdomen that joins the Common bile duct.
The gall bladder stores bile produced by the liver. During meals, especially fatty meals, the gall bladder squeezes out the bile it has stored, into the bile duct.
The bile duct then runs through the pancreas for a bit, and enters the duodenum at ampulla ( also joined by pancreatic duct which drains the digestive juice from the pancreas) where the bile mixes with the food.
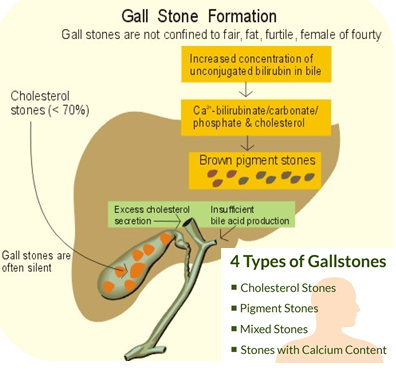
What are gallstones? Causes / Risk factors ?
Female > Male
Age > 40 years
Reproductive Age
Obesity / overweight
RExcess estrogen (pregnancy, OC pills or Hormone replacement therapy)
Biliary infections / Round worms in bile duct
Hemolytic anemis ( sickle cell anemia etc. pigment stones)
Dieting or rapid weight loss (eg after bariatric surgery)
Certain cholesterol reducing drugs eg statins
The presence of gallstones in the gallbladder is called “Cholelithiasis”.
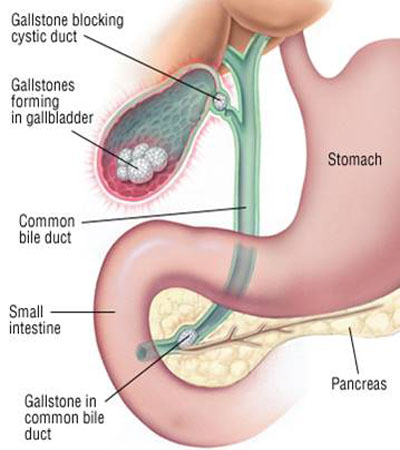
The presence of gallstones in the common bile duct is called “choledocholithiasis”.
Effects of or problems caused by Gallstones ?
In the gallbladder
Asymptomatic / incidentally detected
Biliary colic with periodicity
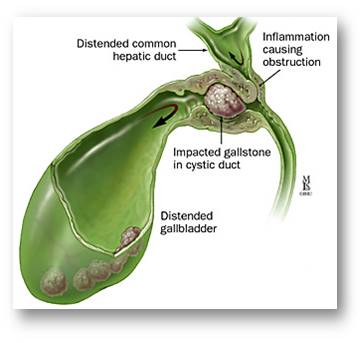
Acute cholecystitis
Chronic cholecystitis
Empyema gallbladder
Perforation causing peritonitis or pericholecystitic abscess
Mucocele of the gallbladder
Carcinoma gallbladder
In Intestine
Gallstone ileus leading to small bowel obstruction
In Bile Duct (CBD)
Obstructive Jaundice
Cholangitis
Acute Gall stone pancreatitis
Is there an alternative to surgery?
Not really
Non-surgical treatments usually do not work, and are offered only to patients who are unfit to undergo surgery.
Stones usually recur after these treatments.
What is the treatment of gallstones ?
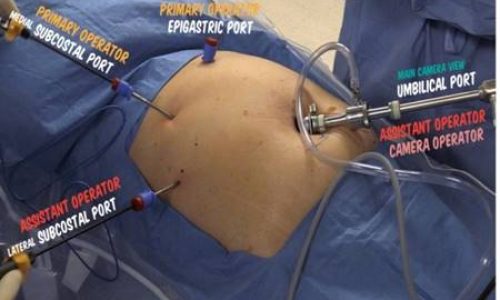
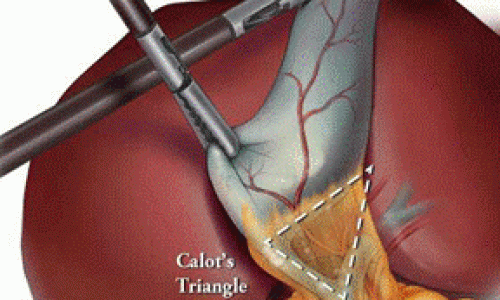
The best treated by an operation that removes the gallbladder i.e. called a Laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Few key holes are made in abdomen, gallbladder is divided from bile duct (which is preserved for bile flow from liver to intestine), surgery usually last 20 to 30 minutes. Patients are started on oral diet on next day or after 6-12 hours from surgery and discharged on next day.
What if I have Common bile duct stones / Jaundice ?
Choledocholithiasis of CBD stones are best treated by 1) ERCP (for removal of CBD stones done endoscopically) follewed by Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. Or by 2) Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy + Laparoscopic CBD exploration along with Flexible choledochoscopy (used to remove CBD stones and used to check complete removal of all stones). Usually a stent is placed within the bile duct that needs to be removed after 4 to 6weeks.
Does it affect one’s digestion if the gallbladder is removed?
Surprisingly, removal of the gallbladder seems to have no effect on the digestive process in the vast majority of patients who undergo this operation. The bile trickles steadily into the gut and helps digest the fatty foods. One should be able to continue eating normally after the operation.